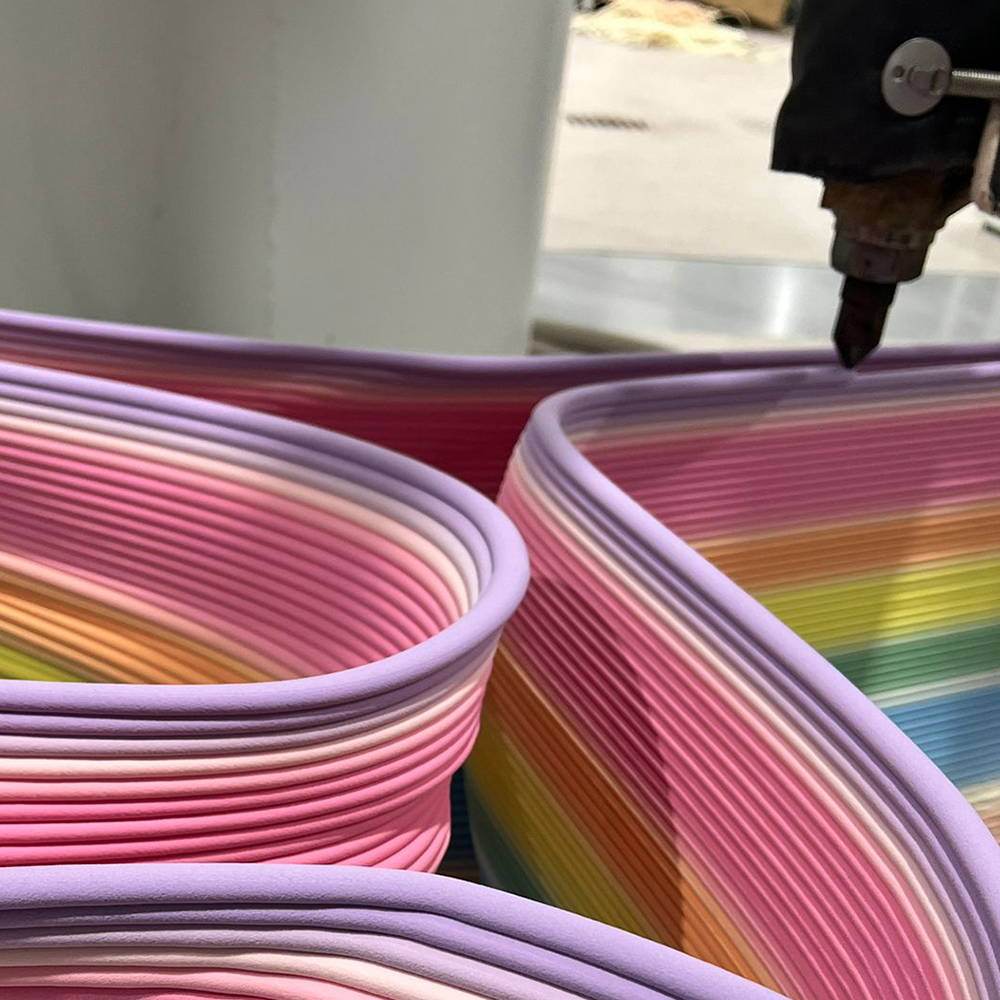
The MAT3D-XL project focuses on developing new thermoplastic materials that are either recycled or bio-based and reinforced with carbon, glass, or natural fibers. These composites enhance the strength and rigidity of printed parts while also promoting circular economy.
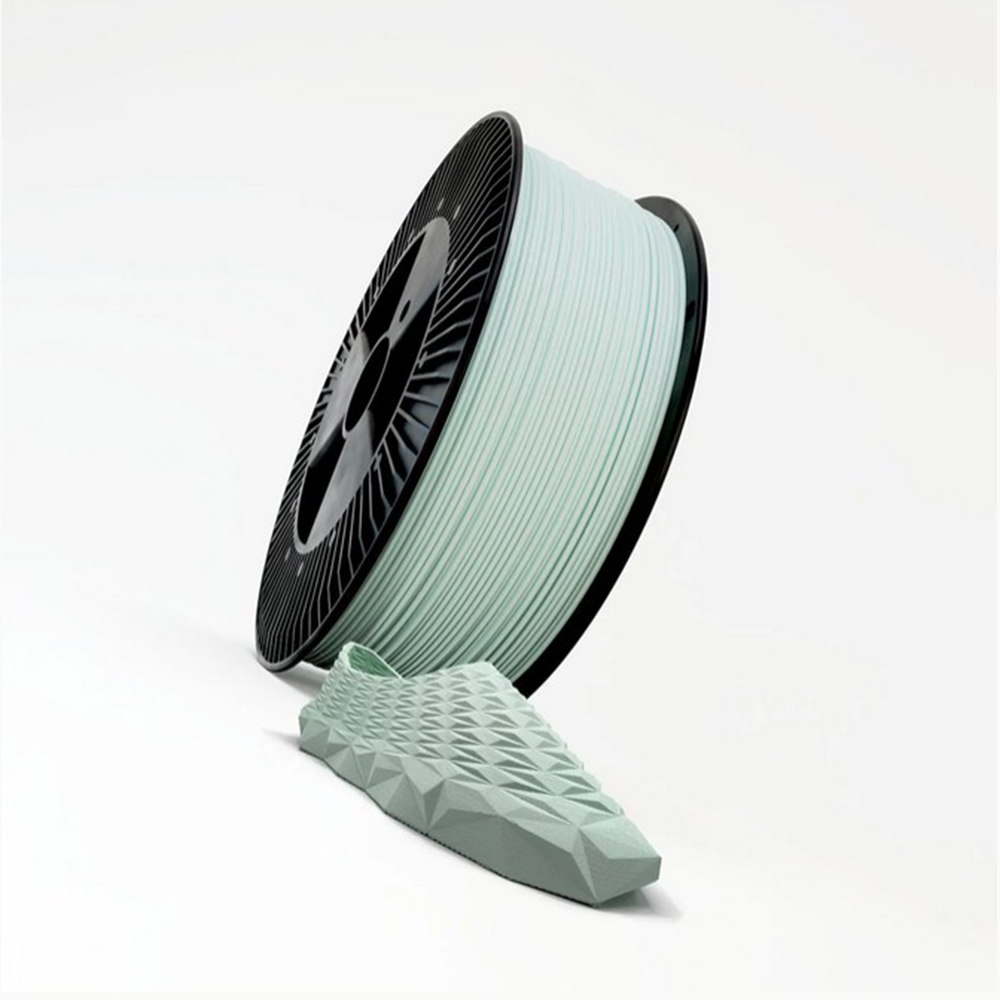
The aim of the Magaya project, meanwhile, is to convert apple pomace, a by-product of natural cider production, into a biopolymer suitable for use in a new Additive Manufacturing process.
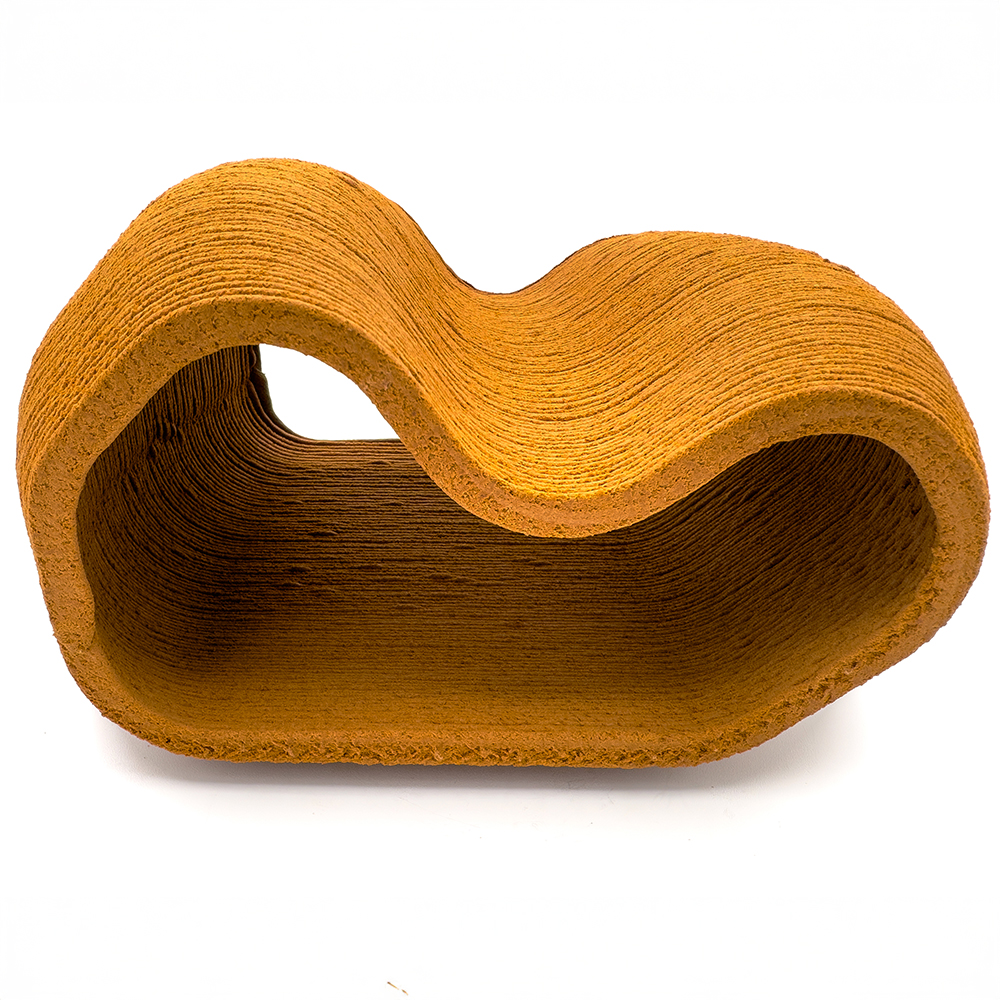
Finally, the Ecofap project aims to develop a new 3D printing material based on recycled natural leather that can be used in various components for fashion, textiles, and footwear. Specifically, the project is focusing on valorizing tanned leather waste from the footwear sector to create new materials for manufacturing soles and heels using FDM. Most of this scrap is usually disposed of in landfills.
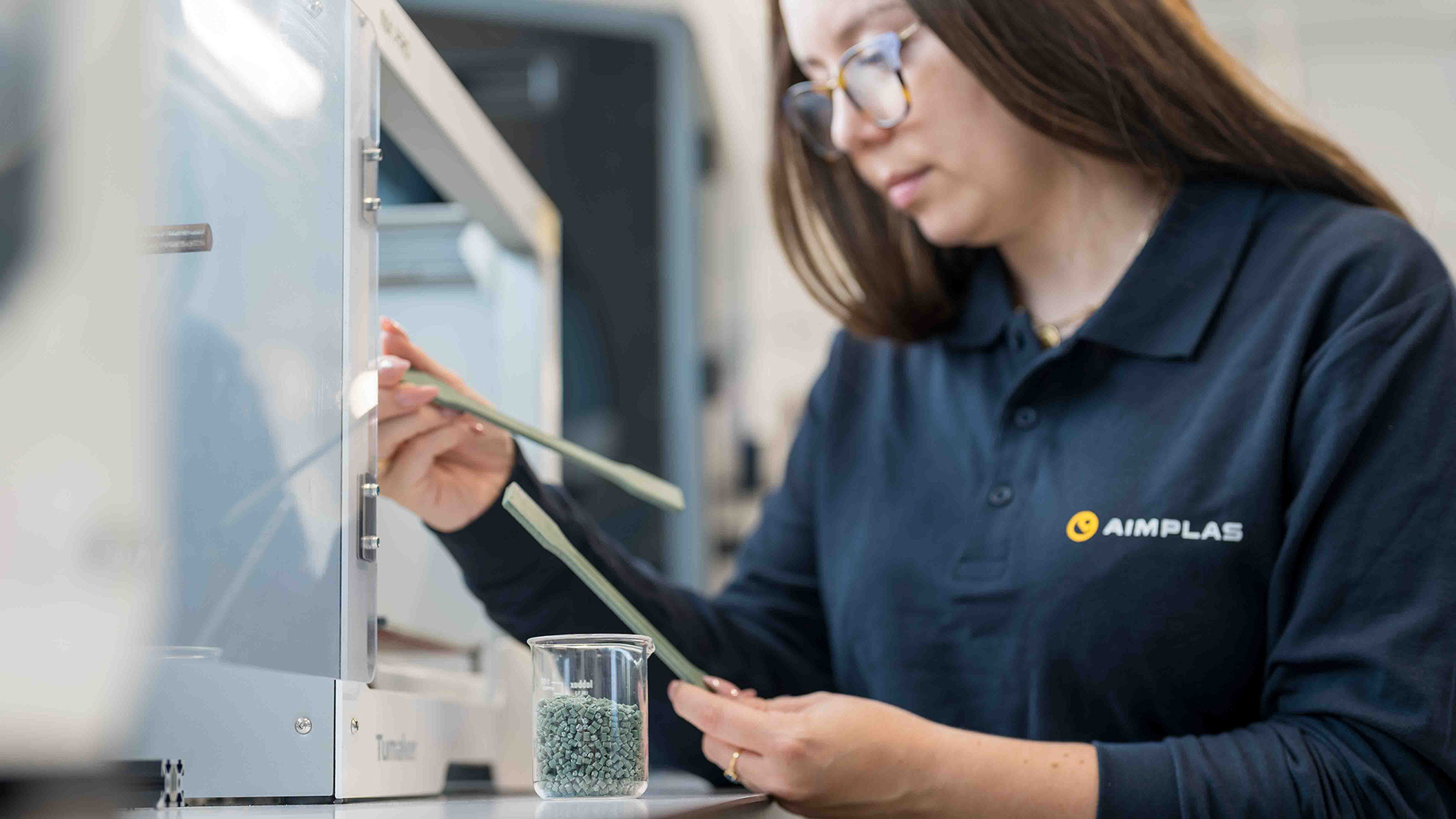
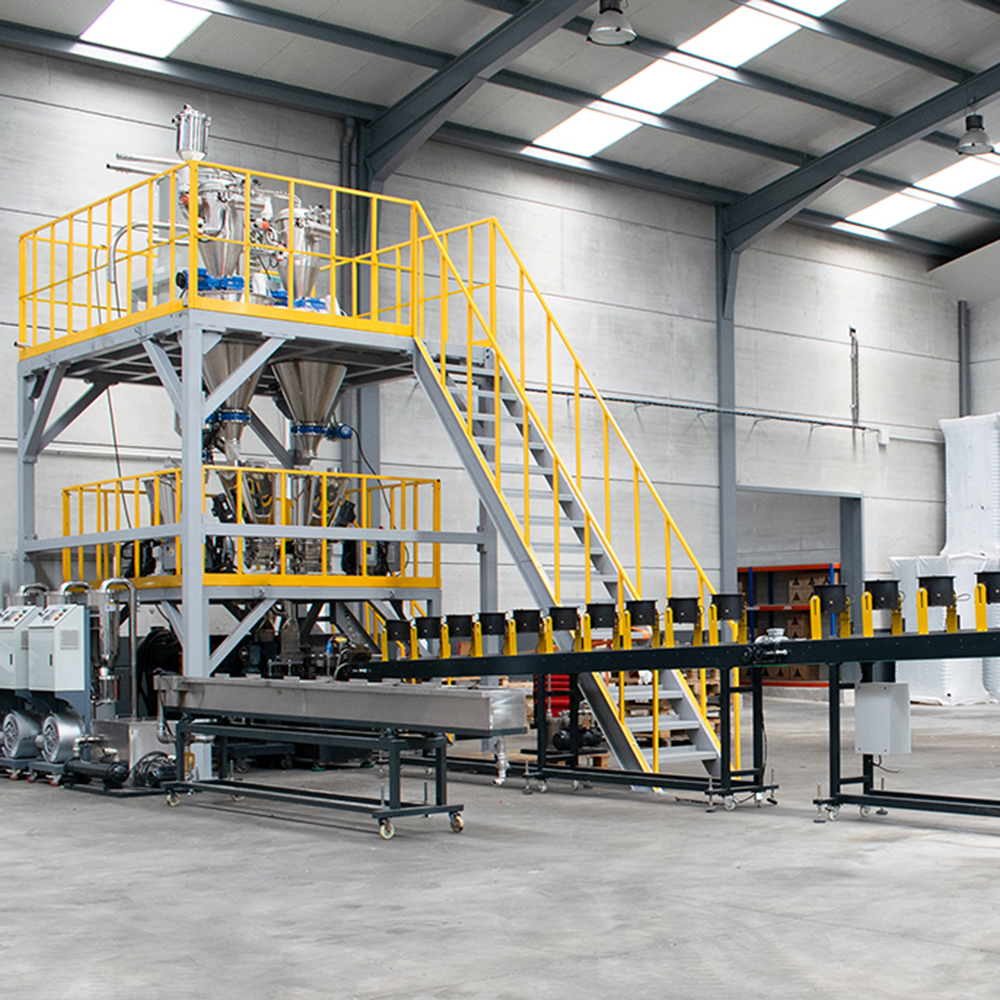
Based in Paterna (near Valencia), Aimplas has been offering solutions along the entire value chain for more than 35 years and has more than 35 pilot plants for plastic processing. These facilities are used for research, the development of new materials, and the improvement of existing processes.
Further company information
Further information
Further exclusive information on Spanish AM companies can be found in the print edition 03/2025 of Formnext Magazine or in the digital Fon Mag:
Aimen, Aimplas, ArcelorMittal, Danobat, HP, IAM3DHub, Indart3D, Madit, Meltio, Reinforce3, Recreus, Smart Materials, Market report Spain