19 June 2023, by Thomas Masuch / Formnext
Additive Manufacturing offers enormous economic potential and can help address current economic and social challenges.
In a world where the importance of digital technologies, sustainability, and secure supply chains continues to grow, companies are facing ever greater demands. Innovations made possible by 3D Printing are playing an important role in addressing these challenges. This unique technology has been a game changer for engineers and product developers, serving as a catalyst for ever more creative products and applications. Layer by layer, objects previously thought impossible are becoming a reality.

3D Printing is a process in which a digital model is turned into a tangible, solid, three-dimensional object, usually by laying down many successive, thin layers of a material. Having been successfully adopted by an ever-growing number of industries, this fairly new technology often offers industry-specific advantages. In some areas, such as dentistry, 3D printing has largely replaced traditional manufacturing methods. The primary fields of application for 3D printing are aerospace, medicine, dentistry, and automotive. Other key industries include consumer goods manufacturing, automation solutions, electronics and electrical engineering, research and higher education, as well as the energy (including oil and gas) and defense sectors.
In addition, companies from other sectors of industry also enjoy opportunities to profit from the market development. For example, numerous traditional companies from the fields of automation, post-processing, and more have already developed and marketed special AM solutions.
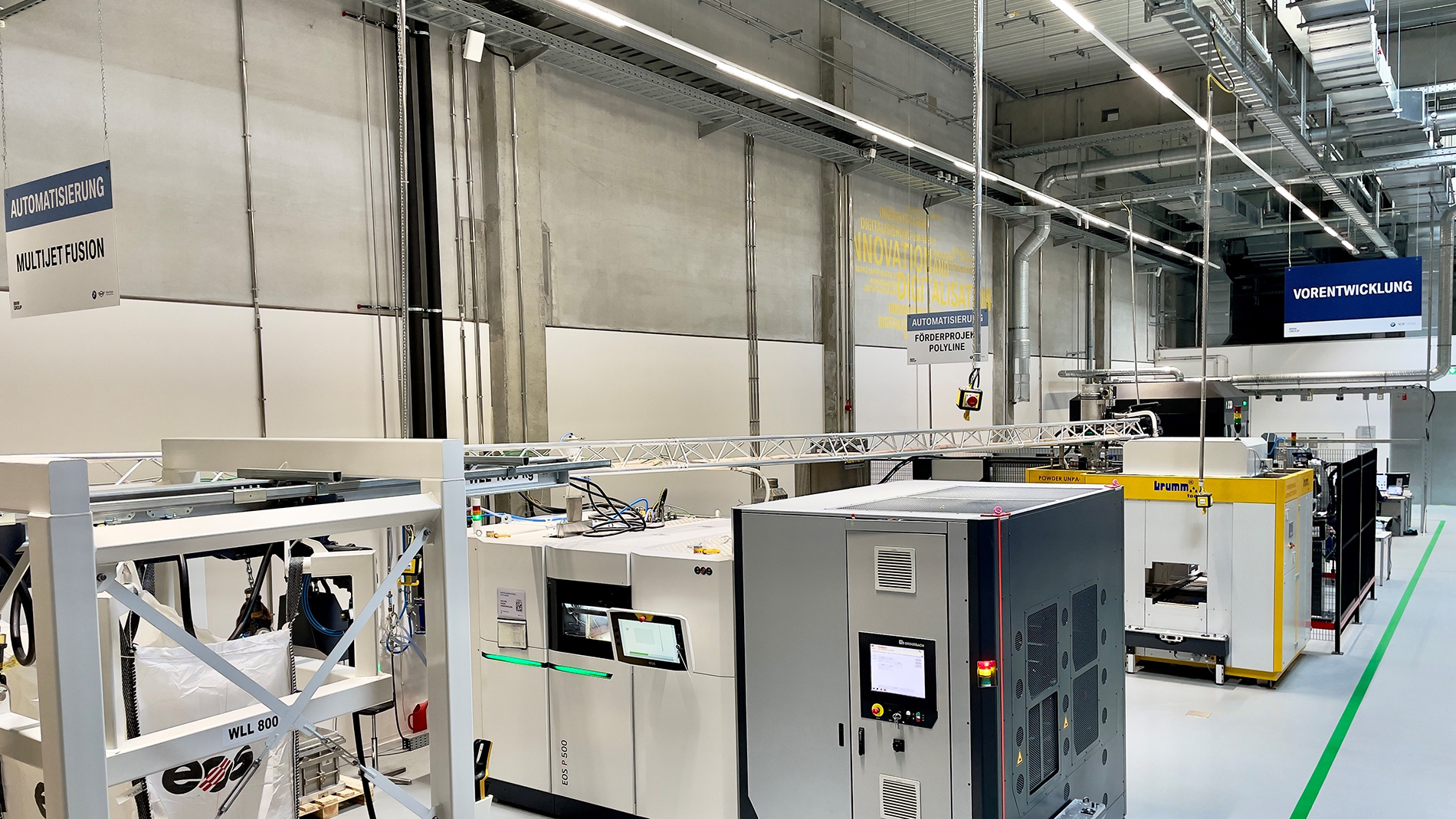
Companies such as BMW are increasingly using Additive Manufacturing in automated systems. This also opens up numerous opportunities for automation specialists. Photo: BMW
Wide range of applications
The diverse applications range from 3D printed rocket engines, automotive components, dentures, and hip joints through to parts for use in mechanical engineering or production equipment. In recent times, there has also been a stark rise in new areas of application. 3D printing in architecture, for instance, is developing rapidly with entire homes and office buildings now being printed. The 3D printing of food and medicines is also becoming a promising field of application. Additive Manufacturing is also providing exciting prospects for the fashion world and numerous other industries.
Additive Manufacturing is helping to shorten development cycles in many industries. For example, conventional manufacturing methods often require costly tool and mold making, resulting in long lead times and high set-up costs. 3D Printing is overcoming these obstacles by enabling rapid prototyping and on-demand production. Complex geometries can be realized effortlessly. This newfound flexibility enables companies to improve designs and drive innovation faster than ever before, further improving their competitiveness.
At the same time, this technology is helping many industrial sectors to operate more efficiently and successfully. Mechanical engineers can improve their products by incorporating 3D printed components. Rockets or aircraft, for example, become lighter thanks to 3D printed components with optimized topology, which ultimately reduces fuel consumption or increases the payload.
Find more articles from the different application areas in our Fon E-Mag:
Electrical engineering and electronics
Mechanical and plant engineering
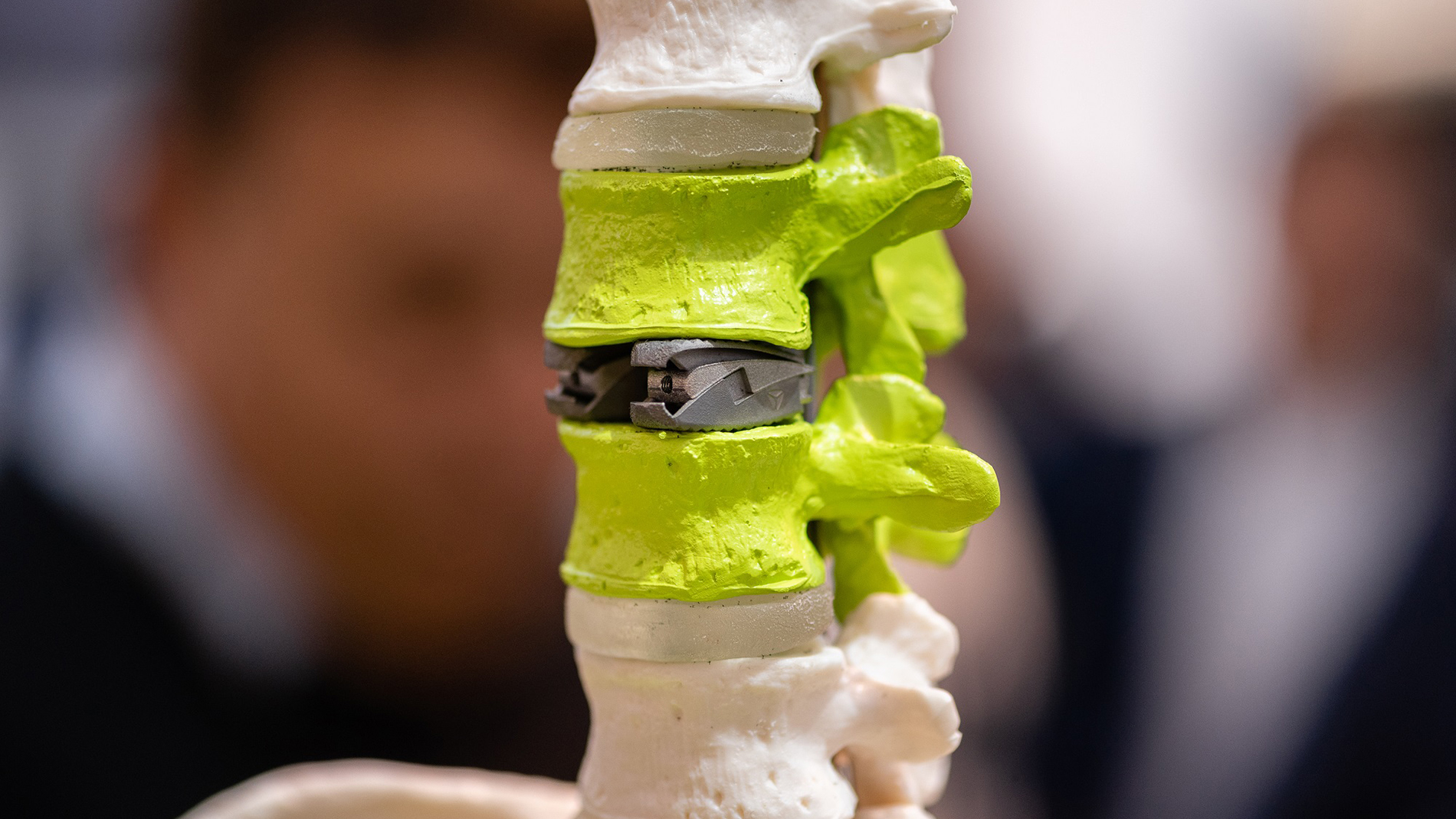
Solutions for the healthcare sector are another growth area for Additive Manufacturing. Photo: Mesago / Mathias Kutt
Sustainability and efficiency
Additive Manufacturing often helps improve the sustainability of products and manufacturing in general and contributes to carbon emissions reductions. There are special tools with which companies can calculate these savings, enabling them to meet necessary savings targets (such as in the automotive industry) for example. Minimal waste is another major sustainability-related advantage of 3D Printing, as it is often only the material in the end product that requires processing. The cost savings resulting from this make AM an interesting prospect for very expensive materials such as titanium. Additive Manufacturing also enables decentralized production. Parts are manufactured exactly where they are needed, thus eliminating the need for transport and warehousing.
Economic significance
In recent decades, the AM industry has experienced double-digit growth almost every year due to the increasingly widespread use of 3D Printing and is now worth around € 20 billion per year. In the next ten years, this volume is expected to rise to more than € 100 billion.
This growth is driven by numerous innovations along the entire process chain, which can also be witnessed at the Formnext exhibition in Frankfurt, held every year in November. Every year, smarter and more specialized software arrives on the market. Ever larger machines and new materials optimized for 3D Printing are enabling new applications such as 3D printed boats or larger, more powerful engines for rockets. Manufacturers also showcase new post-processing and quality assurance solutions designed to make 3D Printing even more efficient and effective in an industrial environment.
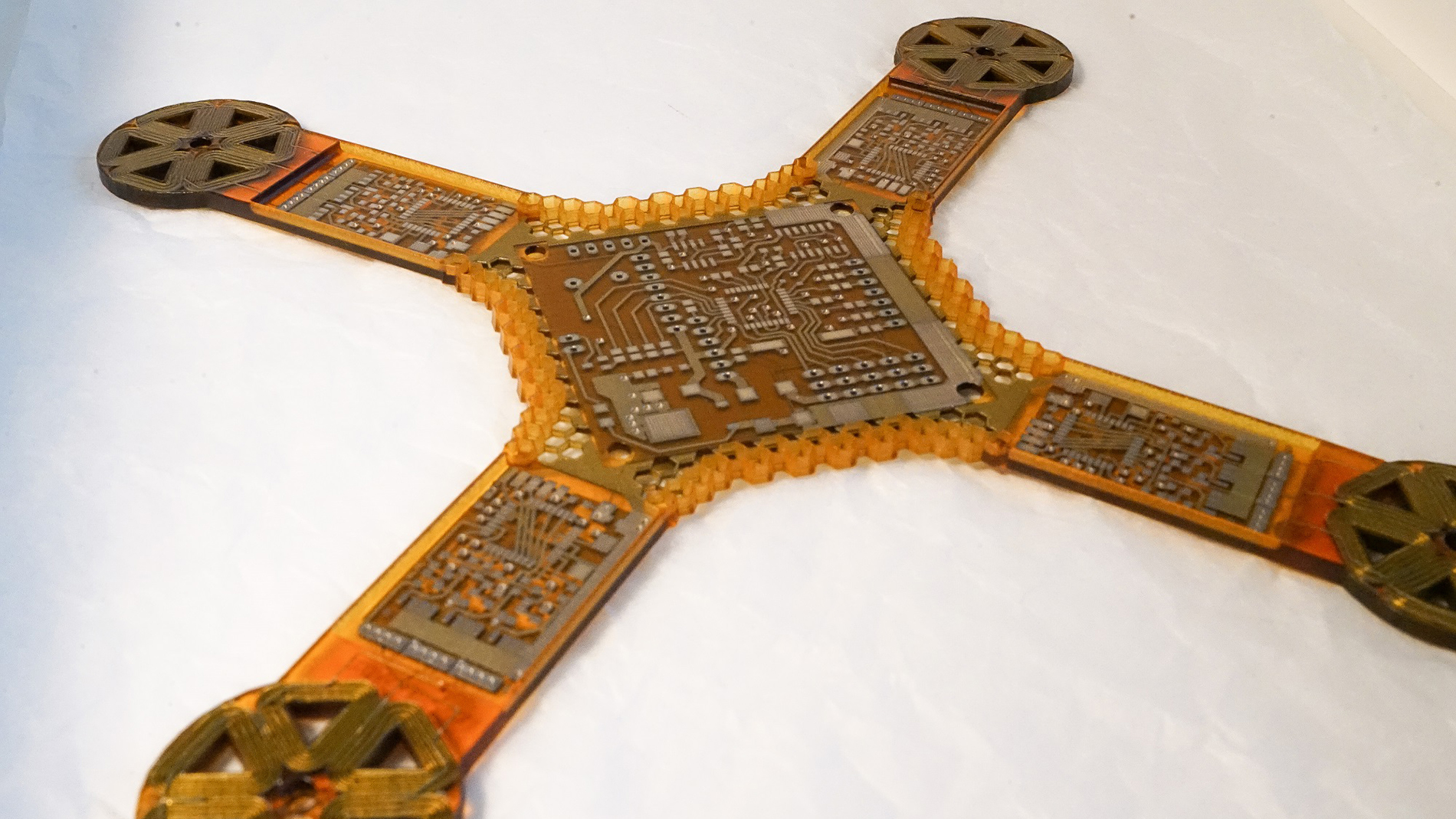
3D Printing of electronics is still a small field of Additive Manufacturing, but it promises enormous potential and a variety of new applications in the near future. The picture shows the basic electronic structure of a drone, including all the conductive tracks and the coils for the motors. Image: J.A.M.E.S.
History and international appeal
The history of 3D Printing dates to the 1980s, when early pioneers like Chuck Hull laid the foundation for the technology. Initially, it was used almost exclusively for the production of prototypes. Over time, however, the industrial production of end products has continued to increase.

The 3D Printing industry now also has a broad international base. Whereas, 20 years ago, plastics printing had its main focus in the United States and companies in Germany were leaders in metal 3D Printing, the industry has now grown to include numerous players from other regions and is very international in scope. Companies from across Europe, China, Australia, and many other countries offer excellent Additive Manufacturing solutions. Other important sales markets include emerging markets such as the Middle East and India.
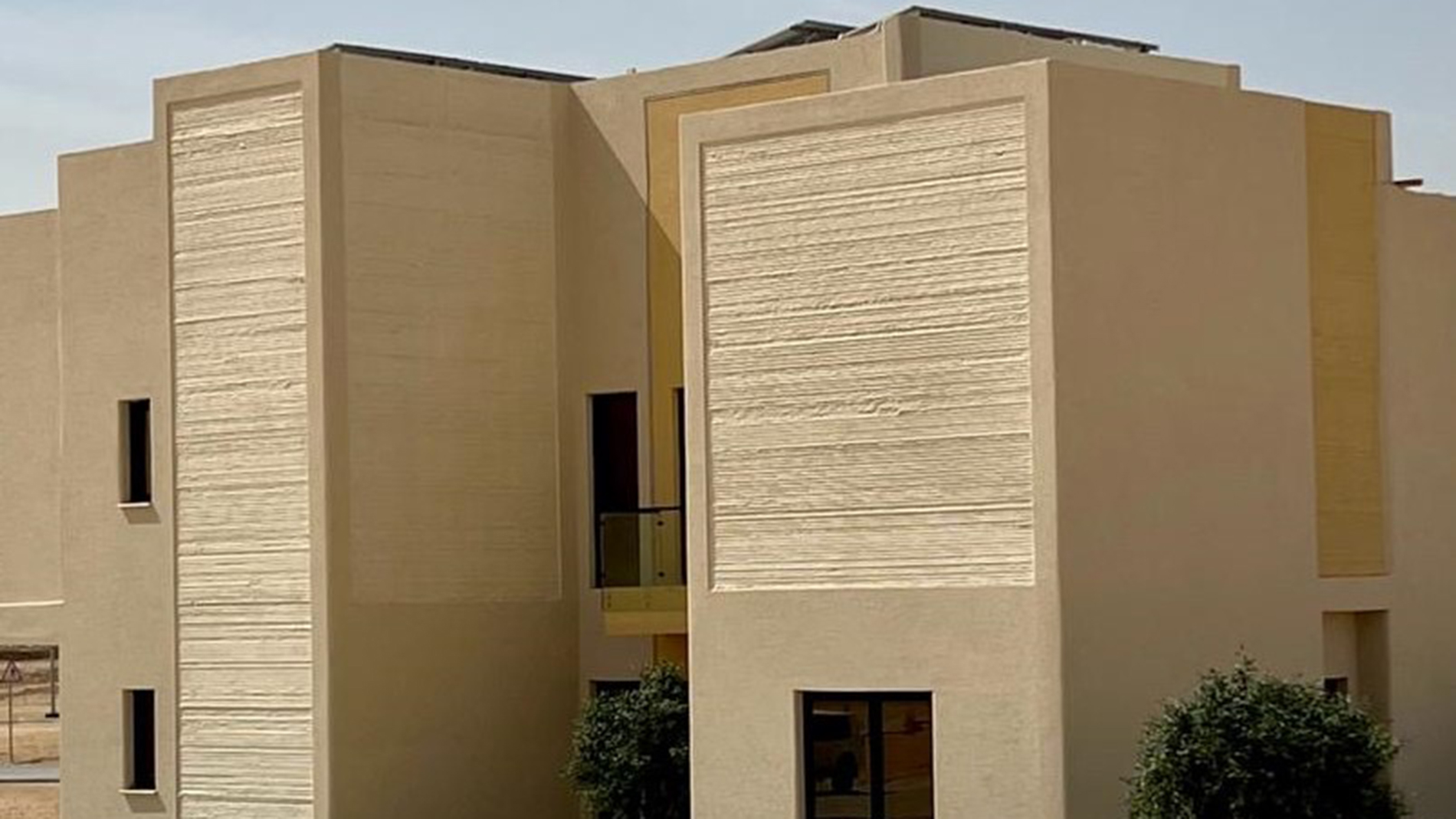
The Middle East has become an important sales market. One of the main applications is 3D Printing of buildings. Here, a 3D printed villa in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Image: Cobod
Outlook
Technological developments and ever greater user creativity (aided by increasing training and education in the field) mean that new 3D Printing applications are emerging all the time at breakneck speed. For manufacturing companies in many industries, the use of 3D Printing is becoming increasingly important and, in some cases, almost indispensable to stay relevant on the market.
The next few years will also see the emergence of numerous hitherto unforeseen applications, especially in the relatively new sectors for 3D Printing, such as construction, food production, and even space exploration. While the 3D Printing of mosques is already planned for the near future, concepts also exist to print habitats in space out of lunar dust. In its relatively short history, the additive industry has already made an enormous impact and will continue to shape our world, layer by layer, in the future.
We will be happy to keep you up to date on current AM developments and the preparations for the formnext exhibition, e.g. with our AM4U newsletter (10x a year) or the Formnext Magazine (Fon Mag). Subscribe free of charge and without obligation to our Industry Insights around Additive Manufacturing.
Tags
- Automotive
- Dental technology
- Additive Manufacturing
- Construction and architecture
- Automation and handling
- Electronic engineering and electronics
