Reading time: 3 minutes

One of the milestones of this collaboration has been the progress achieved in Additive Manufacturing applied to nickel-based alloys and lightweight materials, as well as alloys for high-temperature applications. “Renishaw has always shared with us its experience accumulated with other customers and sectors, understanding the particularities of each alloy and thus enabling us to accelerate the development process,” explains Fernando Lartategui, Associate Researcher in Additive Layer Manufacturing at ITP Aero.
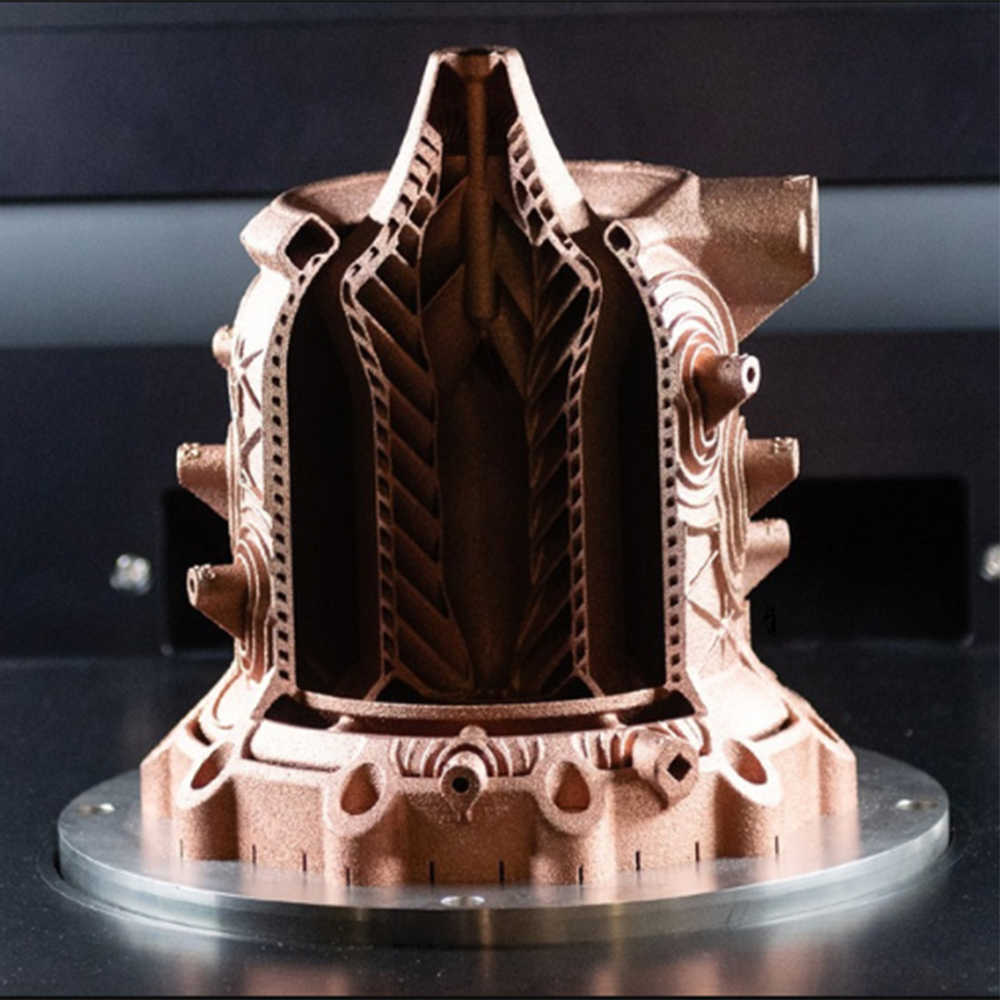
This transfer of knowledge has been essential for developing components such as the Tail Bearing Housing (TBH), one of the two joining elements between the aircraft and the Rolls-Royce UltraFan engine — the largest in the world. Scheduled for the end of the decade, this engine is compatible with 100% sustainable aviation fuels and, compared to the original Trent 700 model, will improve fuel efficiency by 25%.
Certified components
ITP Aero has produced the TBH using Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF). Renishaw’s Solutions Centre in Barcelona contributed its expertise in print preparation and execution, including scanning strategies, parameter development and layout optimization.
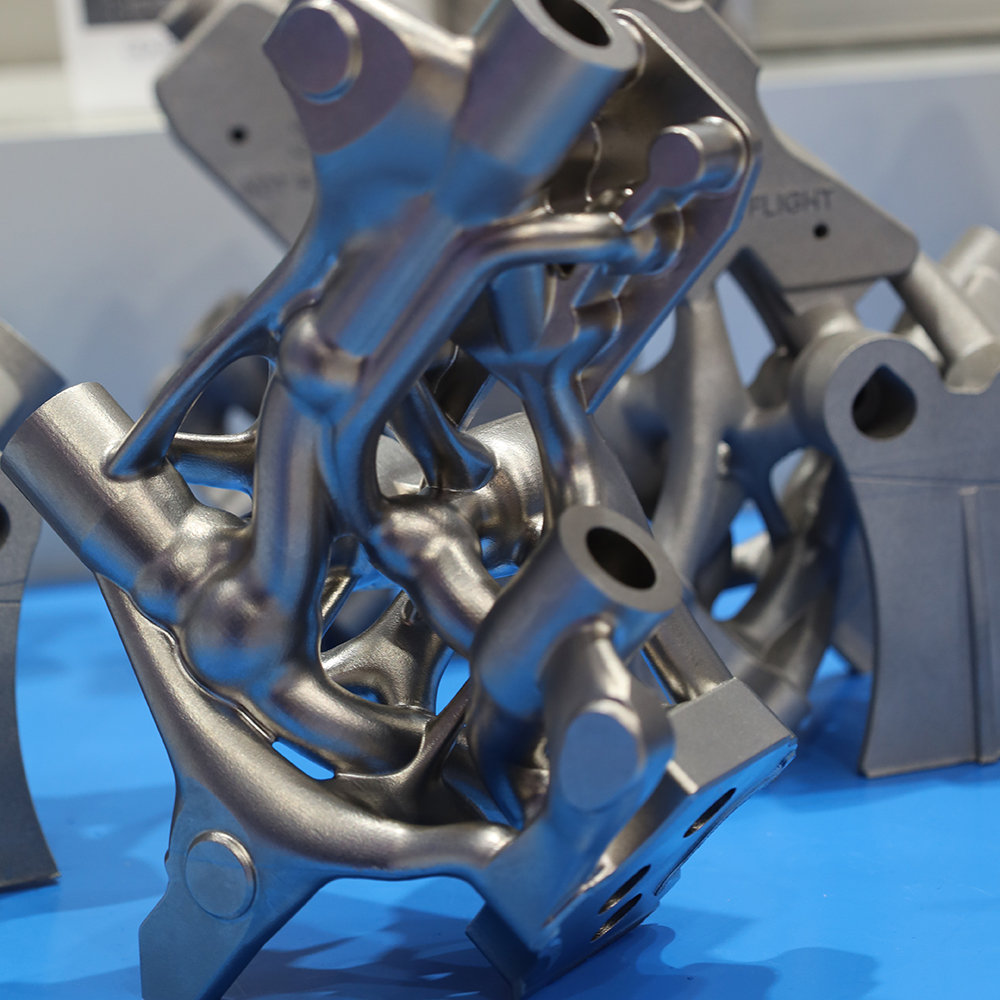
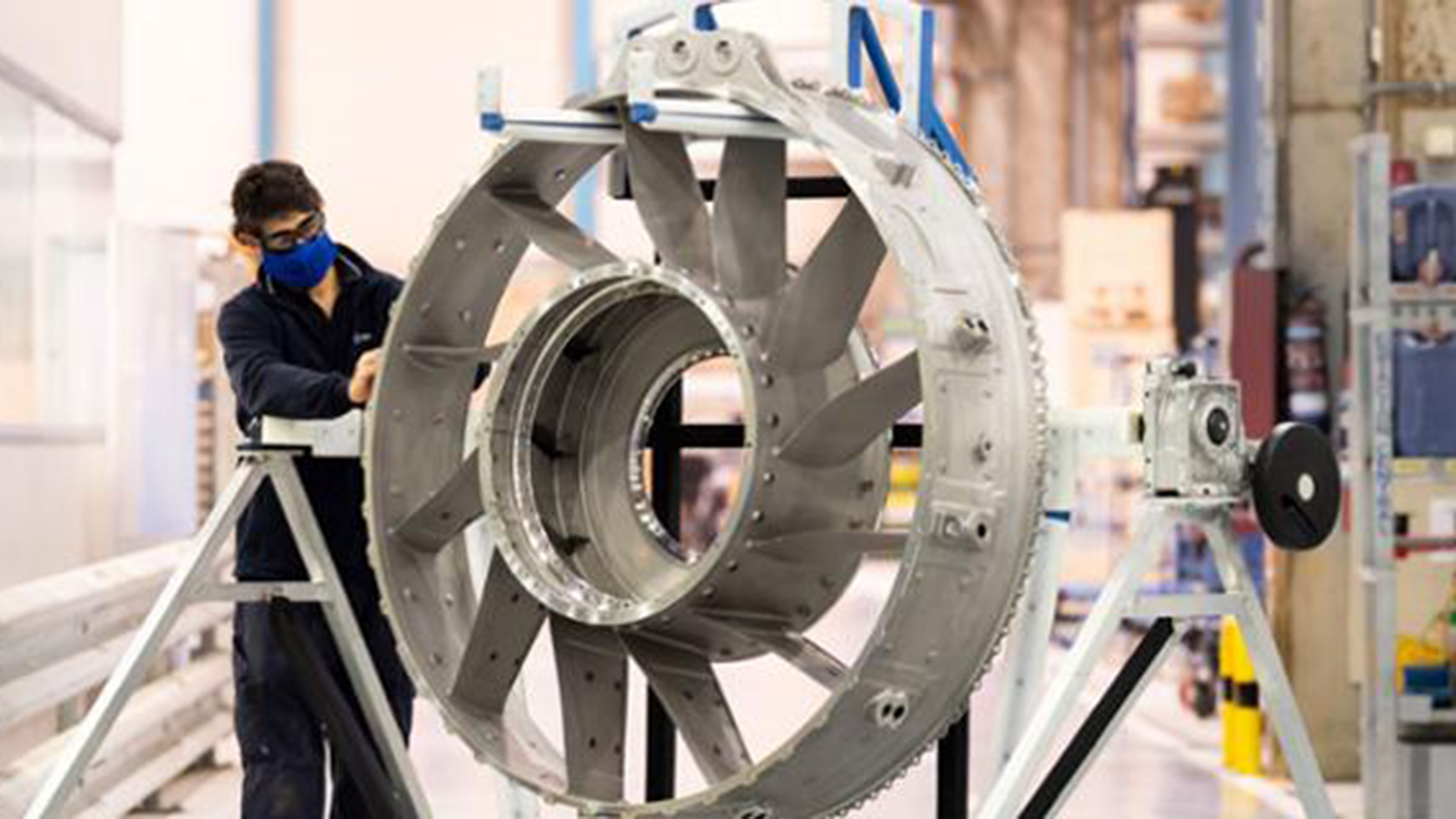
The collaboration between Renishaw and ITP Aero has also contributed to the manufacture of already certified and in-production aerospace components, such as the TP400 engine vanes of the rear engine structure. These were the first structural components produced by Additive Manufacturing, also using LPBF, to be certified by both the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) and the Spanish Aviation Safety and Security Agency (AESA) — a testament to the maturity of this technology in critical industrial environments.
Working alongside Renishaw has also enabled ITP Aero to establish its own internal Additive Manufacturing standards, including specifications and process regulations. This standardization not only provides technical consistency and traceability, but also strengthens confidence in the process.
24 million euros for advanced manufacturing
ITP Aero has also created a new advanced manufacturing centre inaugurated with an investment of €24 million In February 2025. Located at the company’s headquarters in Zamudio (Basque Country), Using AM as one of the four pillars of R&D activity, Admire aims among others to develop solutions for more sustainable aircraft engines, and improve manufacturing process efficiency
Precise tuning of laser parameters
To further improve AM, Renishaw has developed Libertas, a flexible framework that gives freedom to precise tuning of laser parameters, tailored to the requirements of individual applications. “Traditionally, support structures are required for surfaces with a critical angle of 45 degrees or more from the horizontal. With the Support Reduction Package, this threshold has been extended—reducing the critical angle to as little as 5 degrees in certain cases,” explains Benjamin Díaz, Additive Manufacturing Product Manager at Renishaw Ibérica. “Beyond reducing support requirements, this approach also enhances surface finish and mitigates thermal stress by intelligently regulating energy distribution during the build process.”
At Formnext, Renishaw will present a preview of Libertas alongside a complete end-to-end AM cell, a new long-life filtration system for the RenAM 500 series, and Argive’s high-performance microturbine.
Renishaw at Formnext 2025: Hall11.0, Booth C11