Text: Matthew Wood, 3 September 2024
Additive Manufacturing is playing a key role in the ongoing development of Australia’s industry – which is why it receives corresponding support
Australia's manufacturing industry has undergone significant transformations over the past few decades. Once dominated by traditional industries such as automotive and white goods, the sector has seen a shift towards advanced manufacturing technologies, including Additive Manufacturing (AM). This shift is driven by the need for innovation, sustainability, and global competitiveness. Additive Manufacturing, with its potential for customization, reduced waste, and localised production, has emerged as a critical component of Australia’s manufacturing landscape.
The Australian manufacturing industry has historically played a pivotal role in the nation’s economy. As of the latest reports, the manufacturing sector contributes approximately A$100 billion to the Australian economy and employs over 900,000 people. The industry is diverse, encompassing sectors such as machinery and equipment, metal products, chemicals, medical devices, and food and beverage.

However, the sector has faced numerous challenges, including competition from low-cost manufacturing countries, a relatively small domestic market, and high labour costs. These challenges have necessitated a focus on advanced manufacturing technologies and innovation to maintain and enhance the sector’s competitiveness.
Research drives development
The adoption of Additive Manufacturing in Australia can be traced back to the early 2000s, with universities and research institutions leading the way. Organisations such as CSIRO have been instrumental in advancing AM technologies through research and development. One of the early success stories in Australian Additive Manufacturing is the establishment of Lab 22 by CSIRO. Lab 22 serves as a hub for innovation, providing access to state-of-the-art AM facilities and expertise. This initiative has helped numerous Australian companies explore and adopt 3D printing technologies, leading to breakthroughs in various industries, including aerospace, medical devices, and automotive.
Australia’s robust research and development (R&D) framework has been a critical driver of innovation in Additive Manufacturing. Along with CSIRO, numerous universities including RMIT, the University of Sydney, and Monash University have established dedicated AM research centers. These institutions collaborate with industry partners to advance AM technologies and develop new applications. For instance, RMIT University’s Advanced Manufacturing Precinct houses cutting-edge 3D printing facilities and has been pivotal in developing new materials and techniques for AM. The University of Sydney’s Sydney Manufacturing Hub, launched in 2021, features state-of-the-art equipment for metal and polymer AM and fosters collaboration between academia and industry.
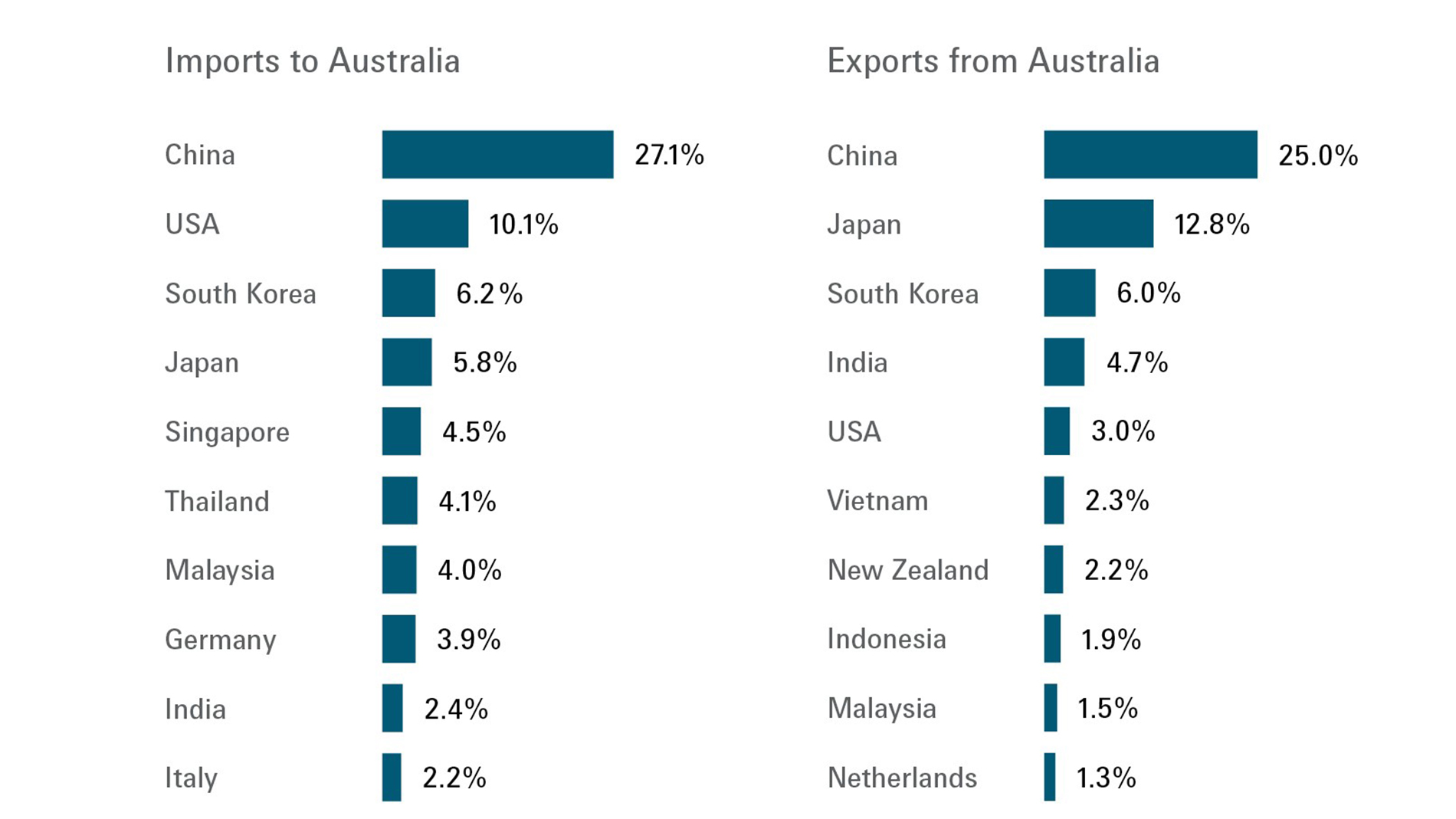
Australia's leading trade partners in terms of import and export percentages. Sources: Handelsblatt, UN Comtrade UN Comtrade
Key AM companies continue to grow
The key players in the industry, including SPEE3D, Titomic, AML3D, Conflux, and Additive Assurance, marked significant milestones and experienced growth in 2023.
SPEE3D made notable advancements in the defence sector, achieving multi-unit sales to five global Defence Forces. They demonstrated the robust capabilities of their machines in extreme conditions, successfully printing metal parts at -20 degrees during the US DoD Point of Need Challenge. Additionally, the shipment of the first XSPEE3D to the UK MTC, which is now showcasing the technology across Europe, was a pivotal moment.
Conflux Technology also achieved several milestones, including launching two new heat exchanger products, securing AS9100D certification, and announcing a serial production customer for a gas-liquid heat exchanger. Conflux received funding from the Australian Space Agency's Moon to Mars Initiative to develop a heat exchanger for rocket engines and from the Australian Research Council to advance nanomaterial coatings and advanced plasma coating technology.
AML3D continued its focused growth strategy, supplying its proprietary Arcemy metal 3D printing technology as a point-of-need manufacturing solution. They concentrated on industrial manufacturers in the US defence, marine, and aerospace industries while scaling up their presence in the USA. This focus led to key milestones, including contracts with the US Navy and Department of Defense, Curtin University, Chevron Australia, and BAE Systems Australia. AML3D also signed a significant reseller agreement with Phillips Corporation, a leading US Federal Government sales partner, to grow its US-based business.

Titomic reinforced its position in the Additive Manufacturing sector, leveraging its core technology, Titomic Kinetic Fusion based on Cold Spray Additive Manufacturing (CSAM). Titomic expanded its CSAM activities in the aerospace sector, marked by the sale of a Titomic ISB system to Epcor and being selected as the supplier of cold spray systems for Airbus. These developments indicate a shift towards adopting cold spray for critical applications. Titomic also announced projects with Boeing and participated in Australia's launch of the SpIRIT satellite, the country's first scientific satellite in two decades.
Overall, the strong emphasis on R&D in Additive Manufacturing positions Australia as a leader in this rapidly evolving field, with significant contributions to technological advancements and economic growth. Additive Manufacturing is reshaping the Australian manufacturing landscape, offering new opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and competitiveness. From aerospace to healthcare, the technology is enabling the production of customized, high-performance components that were previously unattainable with traditional manufacturing methods. By embracing Additive Manufacturing, Australia is not only enhancing its manufacturing capabilities but also paving the way for a more sustainable and resilient industrial future.
Annual growth rate of 23.9 percent
According to a 2023 report by the Australian Department of Industry, Science, Energy and Resources, the Additive Manufacturing market in Australia is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23.9% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is driven by increased investment in R&D, the establishment of advanced manufacturing hubs, and the growing adoption of AM technologies across various sectors, including aerospace, medical, transport and renewable industries.
Acknowledging the transformative potential of Additive Manufacturing, the Australian Government has designated Additive Manufacturing as a critical technology in the national interest, highlighting its significance as an enabling capability for advanced manufacturing. AM holds a prominent position in the priority areas outlined by the National Reconstruction Fund (NRF), emphasizing its importance in driving innovation and value creation across various sectors.
Matthew Wood is Trade Manager Manufacturing and Defense for the Australian state of Global Victoria
FURTHER INFORMATION:
Tags
- Market reports and studies
